jgTextRank : Yet another Python implementation of TextRank
Resources
Details
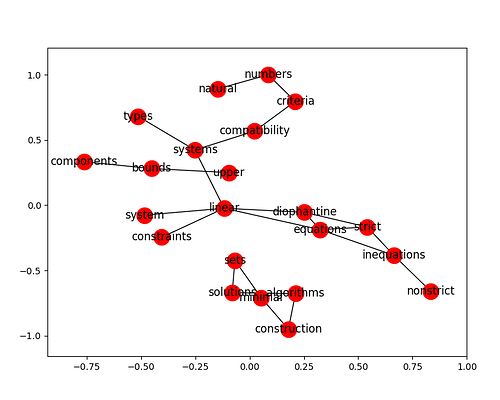
This is a parallelisable and highly customisable implementation of the TextRank algorithm [Mihalcea et al., 2004]. You can define your own co-occurrence context, syntactic categories (choose either “closed” filters or “open” filters), stop words, feed your own pre-segmented/pre-tagged data, and many more. You can also load co-occurrence graph directly from your text for visual analytics, debug and fine-tuning your custom settings. This implementation can also be applied to large corpus for terminology extraction. It can be applied to short text for supervised learning in order to provide more interesting features than conventional TF-IDF Vectorizer.
TextRank algorithm look into the structure of word co-occurrence networks, where nodes are word types and edges are word cooccurrence.
Important words can be thought of as being endorsed by other words, and this leads to an interesting phenomenon. Words that are most important, viz. keywords, emerge as the most central words in the resulting network, with high degree and PageRank. The final important step is post-filtering. Extracted phrases are disambiguated and normalized for morpho-syntactic variations and lexical synonymy (Csomai and Mihalcea 2007). Adjacent words are also sometimes collapsed into phrases, for a more readable output.